Explore the Ancient Roman World
Echoes of the Past

“Historia vero testis temporum, lux veritatis, vita memoriae, magistra vitae, nuntia vetustatis, qua voce alia nisi oratoris immortalitati commendatur?”
"And as History, which bears witness to the passing of the ages, sheds light upon reality, gives life to recollection and guidance to human existence, and brings tidings of ancient days. whose voice, but the orator's, can entrust her to immortality?”
"And as History, which bears witness to the passing of the ages, sheds light upon reality, gives life to recollection and guidance to human existence, and brings tidings of ancient days. whose voice, but the orator's, can entrust her to immortality?”
- Cicero, De oratore, 2.36
LATEST ARTICLES
Three Artifacts that illustrate legacy of Western Roman Empire
One of the greatest civilizations in history, the Roman Empire, left behind a vast legacy that still influences our world today. The Edict of Milan, the Twelve Tables of Roman Law, and Roman roads are three items that stand out among its many contributions for their enduring influence. The Edict of Milan, which was issued in 313 CE and established religious freedom and officially legalized Christianity within the Roman Empire, ending centuries of persecution; the Roman roads, which used innovative engineering techniques to build an impressive network of over 80,000 kilometers of paved roads; and the Twelve Tables, which were the first written laws to be publicly displayed and applied to all citizens, giving the lower classes greater legal rights and protections. These astonishing accomplishments demonstrate how inventive Roman culture was and how its influence can still be seen in modern infrastructure, legal systems, and religious freedoms.
The Edict of Milan, issued in 313 CE by Emperors Constantine I and Licinius, marked a turning point in...
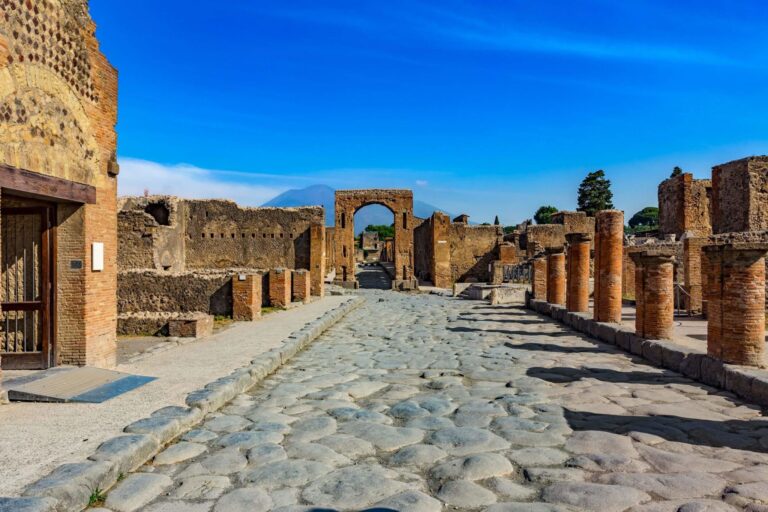
Roman roads are among the most impressive achievements of ancient engineering, forming the most advanced...
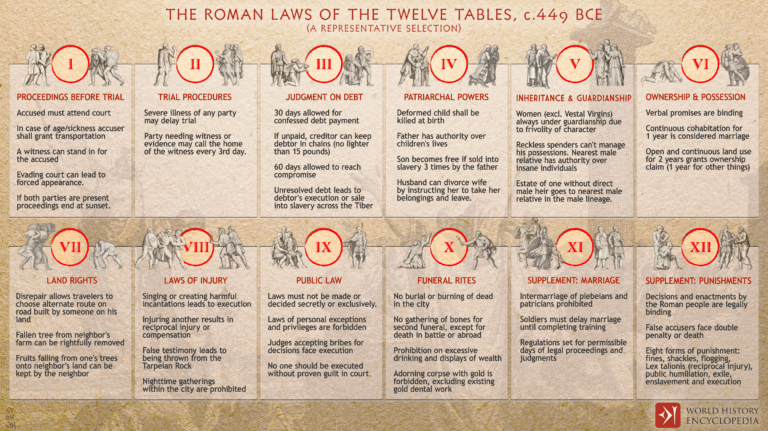
The Law of the Twelve Tables, which originated in 451-450 BCE during the Roman Republic, is the oldest...
The legacies of the Roman Empire are still alive through its innovations in infrastructure, religion, and law. Roman roads symbolize technological excellence and the power of connectivity. The Edict of Milan introduced the world to the value of religious freedom, changing the course of Western religious history. The Twelve Tables established the idea that laws should be public, written, and applied to all people equally—an idea that is still central to legal systems today. Each of these artifacts demonstrates how Rome’s influence went beyond military conquest and political control; it shaped the fundamental ideas and systems of modern civilization. By examining these artifacts, it becomes clear that the Roman Empire’s achievements reached far beyond its borders and era, shaping not only its own society but also those of future civilizations.
Three Artifacts That Signaled the Decline of the Western Roman Empire
Hadrian’s Wall, together with Diocletian’s Edict on Maximum Prices and the Arch of Constantine, symbolizes the key stages in the decline of the Roman Empire. The construction of Hadrian’s Wall demonstrates Rome’s shift from aggressive expansion to defensive military strategies. The Diocletian Price Edict established price controls to curb inflation and stabilize the economy. The Arch of Constantine reflects the political and religious transition in Rome by honoring domestic triumphs instead of foreign conquests. It also signals the rising influence of Christianity, which played a role in the division of the empire. Together, these artifacts reveal how mounting military pressures, economic instability, and religious transformation contributed to the fall of the Western Roman Empire.
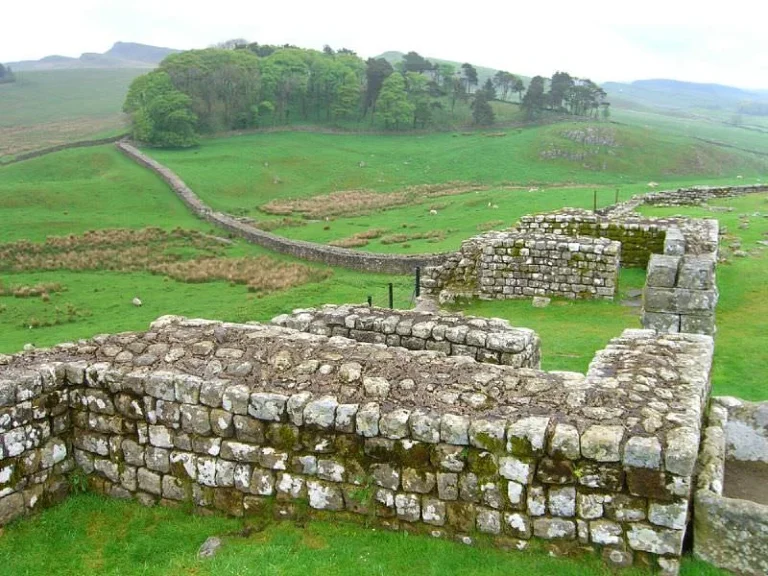
Hadrian’s Wall stretches from the east to the west coast of northern Britain, spanning approximately...
The Edict on Maximum Prices, issued by Emperor Diocletian in 301 CE, was one of the most ambitious economic...
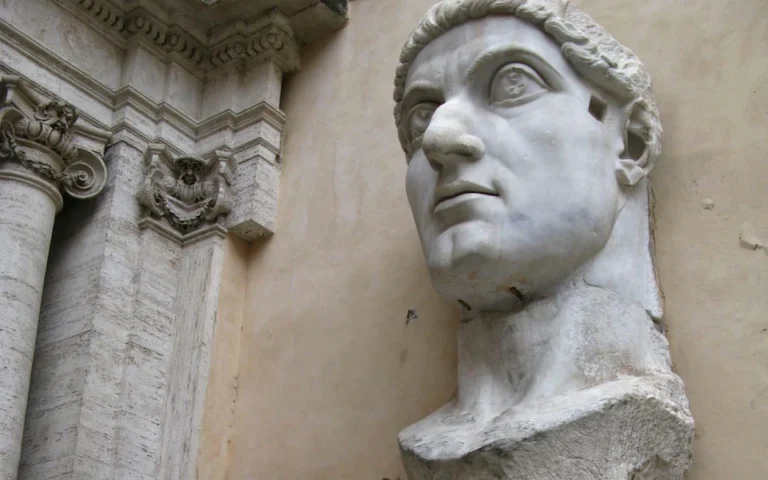
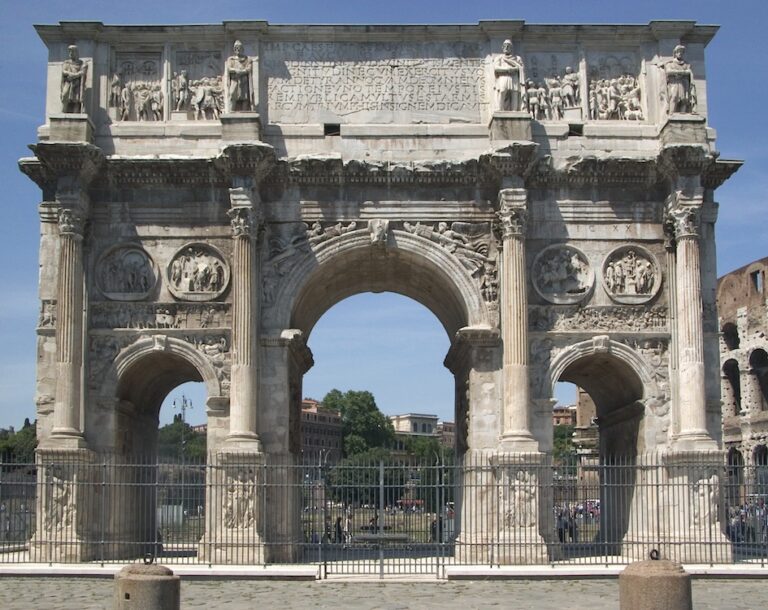
The Arch of Constantine is a triumphal arch constructed near the Colosseum in Rome, under the orders...
Trajan Decree to Dacians after battle of Sarmizegetusa (102 AD)?
The First Dacian War ended without a surviving decree from Emperor Trajan to the Dacians, but historical sources confirm that the peace settlement imposed major terms on King Decebalus, including territorial concessions, the stationing of Roman garrisons, and his submission as a client king under Roman control. This blog explores how such a decree might have looked if it had ever existed.
Emperor Trajan’s victory at the Battle of Sarmizegetusa in 102 AD became the critical moment that...
Three the most significant artifacts
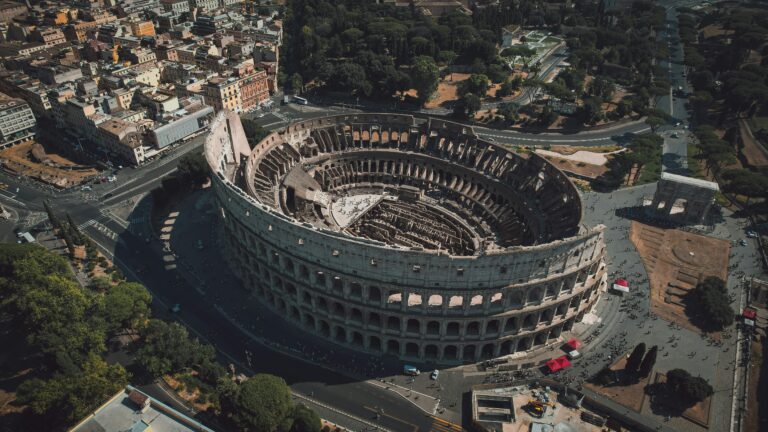
The Roman civilization was one of the most influential in history. Major developments that shaped it include the Colosseum, which served as both a grand entertainment venue and a political tool for emperors; aqueducts, which transformed urban water supply by providing a steady source of clean water; and the Julian calendar, which improved timekeeping with a more accurate and predictable system. These achievements played a significant role in the strength and longevity of the Roman Empire.
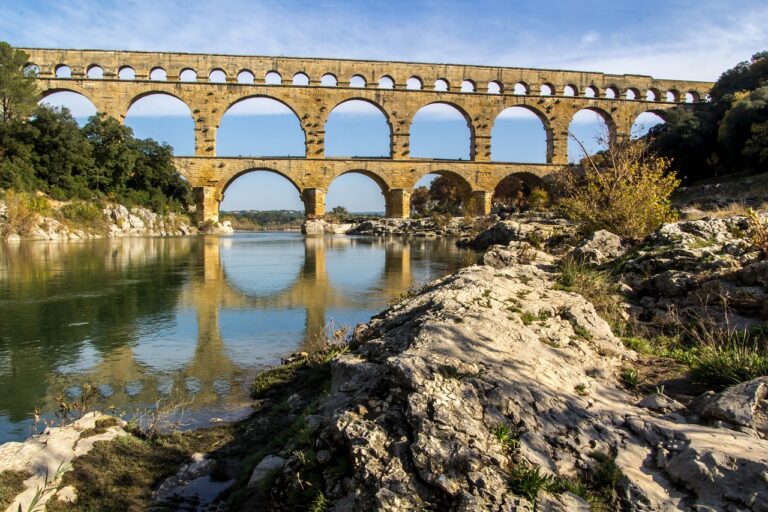
The Roman aqueducts were an advanced water supply system that used a vast network of pipes, tunnels, bridges, and canals to transport fresh water from distant sources, such as lakes...
The Julian calendar, introduced by Julius Caesar in 46 BCE and adopted in 45 BCE, replaced the inaccurate lunar-based Roman calendar with a solar-based system. Used in Europe for over...
Lets connect!
I look forward to speaking with you. Let’s explore the ancient Roman world together! Please share your opinions on the current content and suggestions for my future blog posts.